What Are the Components of a House's Underground and Above-Ground Structures?

Table of Contents
- Introduction to House Structure
- What Is a House Structure?
- Table Separating Underground and Above-Ground Structures
- Underground Structure
- Above-Ground Structure
- Conclusion
Introduction to House Structure
Building a house is a process that requires knowledge and expertise in many areas. One of the most important aspects is the house structure, which serves as the foundation that ensures the house is strong and safe. Understanding the components of both the underground and above-ground structures will help you plan and maintain your home more effectively. In this article, we will introduce you to the various components of a house structure and explain the function of each part in detail.
What Is a House Structure?
The house structure refers to the system composed of various parts that work together to support the weight and forces acting upon the house, including the weight of the house itself, its occupants, and environmental forces like wind and earthquakes. The house structure is divided into two main parts: the underground structure and the above-ground structure. Each part has its importance and distinct functions.
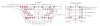
Table Separating Underground and Above-Ground Structures
| Underground Structure | Above-Ground Structure |
|---|---|
| 1. Pile | 1. Floor |
| 2. Foundation | 2. Column |
| 3. Pedestal | 3. Main Beam |
| 4. Ground Beam | 4. Secondary Beam |
| 5. Wall | |
| 6. Roof Structure |
Underground Structure
The underground structure is the part located beneath the ground surface. It serves to support the entire weight of the house and transfer it to the soil. The main components of the underground structure include:
1. Pile
Piles are structural elements driven deep into the ground. They function to receive the load from the house and transfer it to stronger soil layers. There are various types of piles, such as driven piles, bored piles, and vibrated piles. The choice of pile depends on soil conditions and the load that needs to be supported.
2. Foundation
The foundation sits atop the piles and connects them to the above-ground structure. It functions to distribute the load from the above-ground structure down to the piles. Foundations come in various forms, such as spread footings and pile caps. Designing the foundation requires consideration of the load to be supported and soil conditions.
3. Pedestal
The pedestal is a short column situated on the foundation. It supports the ground beam and the above-ground structure. The pedestal receives the load from columns and beams and transfers it down to the foundation and piles.
4. Ground Beam
The ground beam is placed on the pedestals at ground level. It connects the pedestals and supports walls or other structures. The ground beam helps distribute loads and adds strength to the underground structure.
Above-Ground Structure
The above-ground structure is the part located above the ground surface, visible and utilized by occupants. Its main components include:
1. Floor
The floor is the surface on which we stand or place objects. It supports the weight of occupants and furniture. Floors can be made of concrete or wood, depending on design and use. They must be strong and level for safety and aesthetics.
2. Column
Columns are vertical structural elements that receive loads from beams and the roof structure, transferring them down to the pedestals and foundation. Columns are crucial for maintaining the stability and strength of the house. Materials used can include reinforced concrete or steel.
3. Main Beam
The main beam is a horizontal structural element placed on top of columns. It receives loads from secondary beams and the floor, transferring them down to the columns. Main beams must be very strong as they support significant loads.
4. Secondary Beam
Secondary beams rest upon the main beams and receive loads from the floor and walls, transferring them to the main beams. They help distribute loads and add strength to the structure.
5. Wall
Walls separate rooms or the interior from the exterior of the house. They support their own weight and may assist in supporting loads from the roof structure. Walls can be made from various materials, such as concrete blocks, concrete, or wood. Additionally, walls play a role in weather and sound insulation.
6. Roof Structure
The roof structure supports the roof and protects the house from rain, sun, and wind. It consists of rafters, purlins, and roofing materials. Materials used for the roof structure can be wood or steel, depending on design and occupant preferences.
Conclusion
The house structure is the most critical aspect of building a house, serving as the foundation that ensures strength and safety. Understanding the components of both the underground and above-ground structuressuch as piles, foundations, pedestals, ground beams, floors, columns, main beams, secondary beams, walls, and the roof structurehelps in planning construction and maintenance.
Selecting appropriate materials and design for each part of the house structure enhances strength, durability, and safety. Therefore, it's advisable to consult experts or experienced engineers in construction to achieve a high-quality house that meets your needs.